Kaua‘i
Near the geographic center of Kauaʻi is one of the wettest known places on earth, Mount Waiʻaleʻale. Despite this, wildfires can and do occur on the island. Steep slopes, rough terrain, difficult access, a large percentage of highly ignitable invasive grasses, and numerous threatened and endangered native species characterize the Kauaʻi landscape.
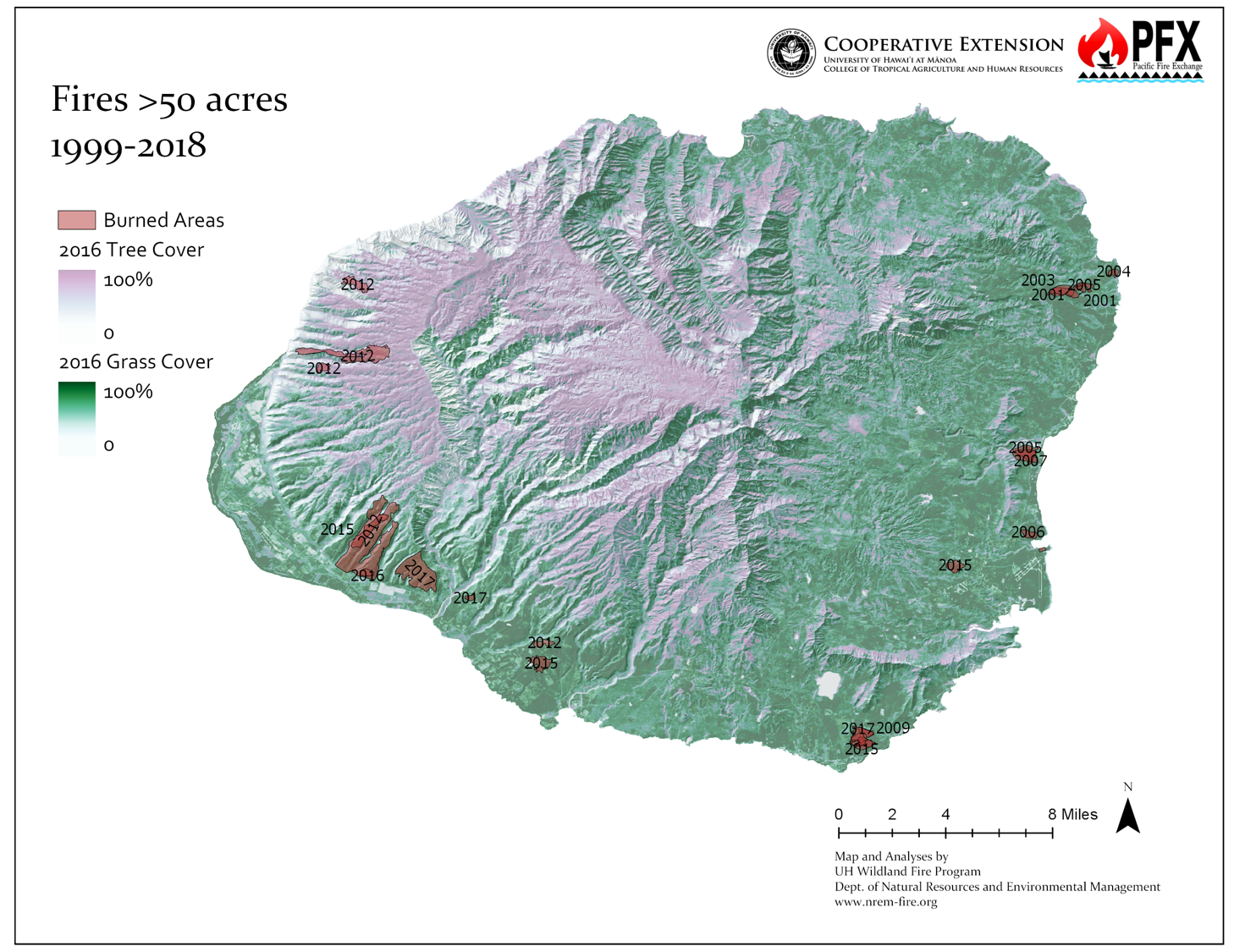
Ignitions occur regularly in the inhabited areas of the island, mostly near the coasts, where the landscape is dominated by current and former agricultural lands as well as grass and brush.
Kauaʻi is among the oldest high Hawaiian Islands and has been shaped by significant erosion, creating its dramatic landscape of valleys. Some of the steepest and least accessible areas include the North Shore to the West side, which also correspond strongly with the highest concentration of threatened and endangered species. This creates a challenging environment for reaching and containing fires when they occur, and presents a risk to the resident endangered species. >> READ MORE
After fires burn through an area of native vegetation in Hawaiʻi, the rebounding vegetation is generally dominated by fast growing non-native grasses and shrubs. Not only does this negatively impact biodiversity, but this can also contribute to erosion and the risk of landslides especially on the steep slopes of Kauaʻi.
The biggest large fires have historically occurred on the lee slope of the eastern flank of Waimea valley. This presents a concerning fire risk for the drought-prone community of Kekaha.
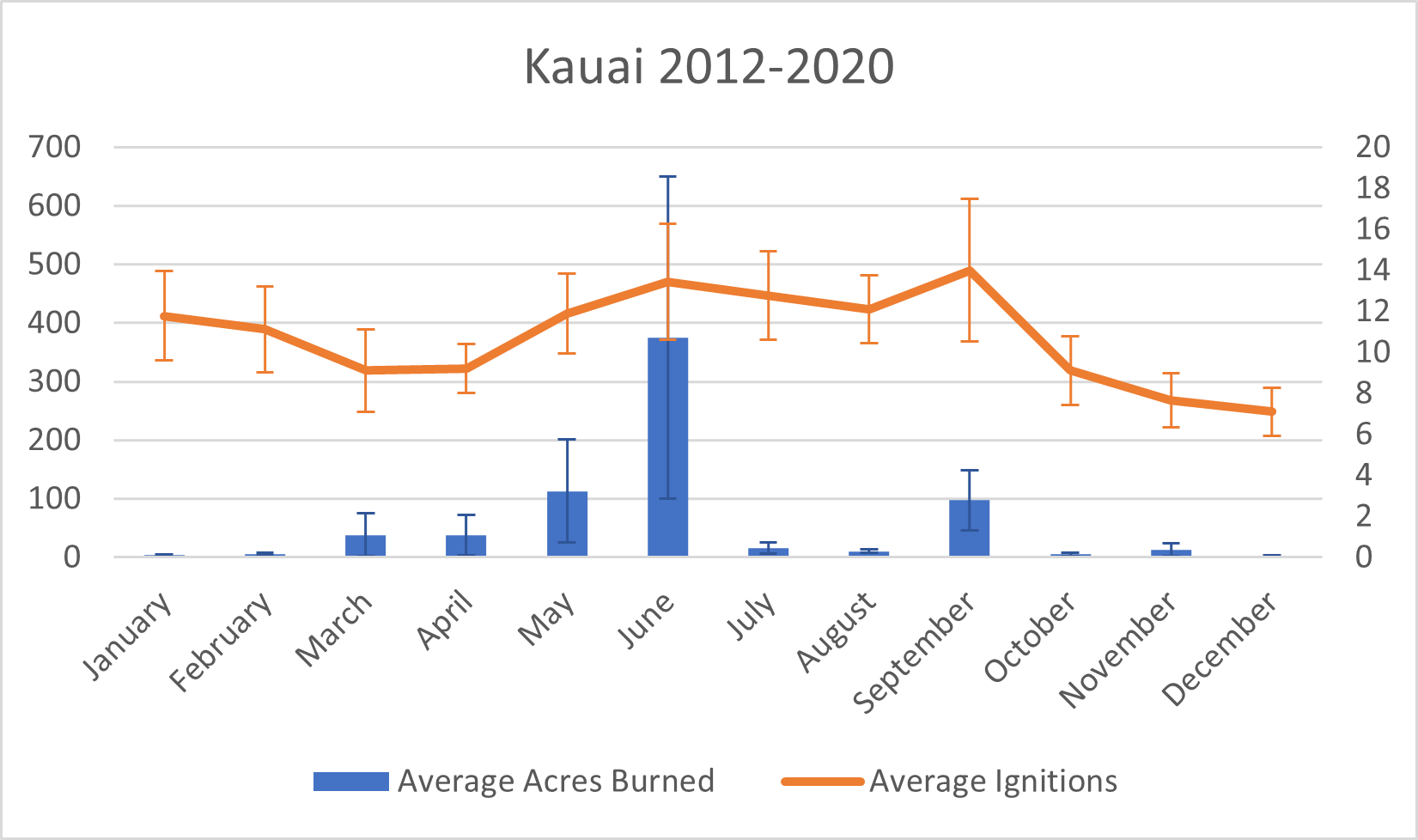
Kauaʻi is known for its high rainfall, but annual rainfall is not always a good indicator for risk. Particularly wet periods over a rainy season can, counterintuitively, significantly elevate hazard levels. Increased precipitation may lead to a surplus of vegetation growth, becoming potential fuel during subsequent drier periods, thereby elevating the risk of large wildfires. Given the changing wind and rainfall patterns arising from climate change, this may lead to increased risk for Kauaʻi.
Recent Resources For Hawai‘i
We measured fuels (live and dead fuel loads, type, height and continuity) and modelled potential wildfire behaviour (flame height and rate of spread) inside and outside of 13 ungulate exclosures, three of which received active ecological restoration (e.g. planting of native shrubs and trees), across a 2,740 mm mean annual rainfall (MAR) gradient on the Island of Hawaii. Differences in fuel characteristics and modelled wildfire behaviour inside versus outside of ungulate exclosures were assessed using linear mixed effects analyses.
- « Previous
- 1
- …
- 24
- 25
- 26