Kaua‘i
Near the geographic center of Kauaʻi is one of the wettest known places on earth, Mount Waiʻaleʻale. Despite this, wildfires can and do occur on the island. Steep slopes, rough terrain, difficult access, a large percentage of highly ignitable invasive grasses, and numerous threatened and endangered native species characterize the Kauaʻi landscape.
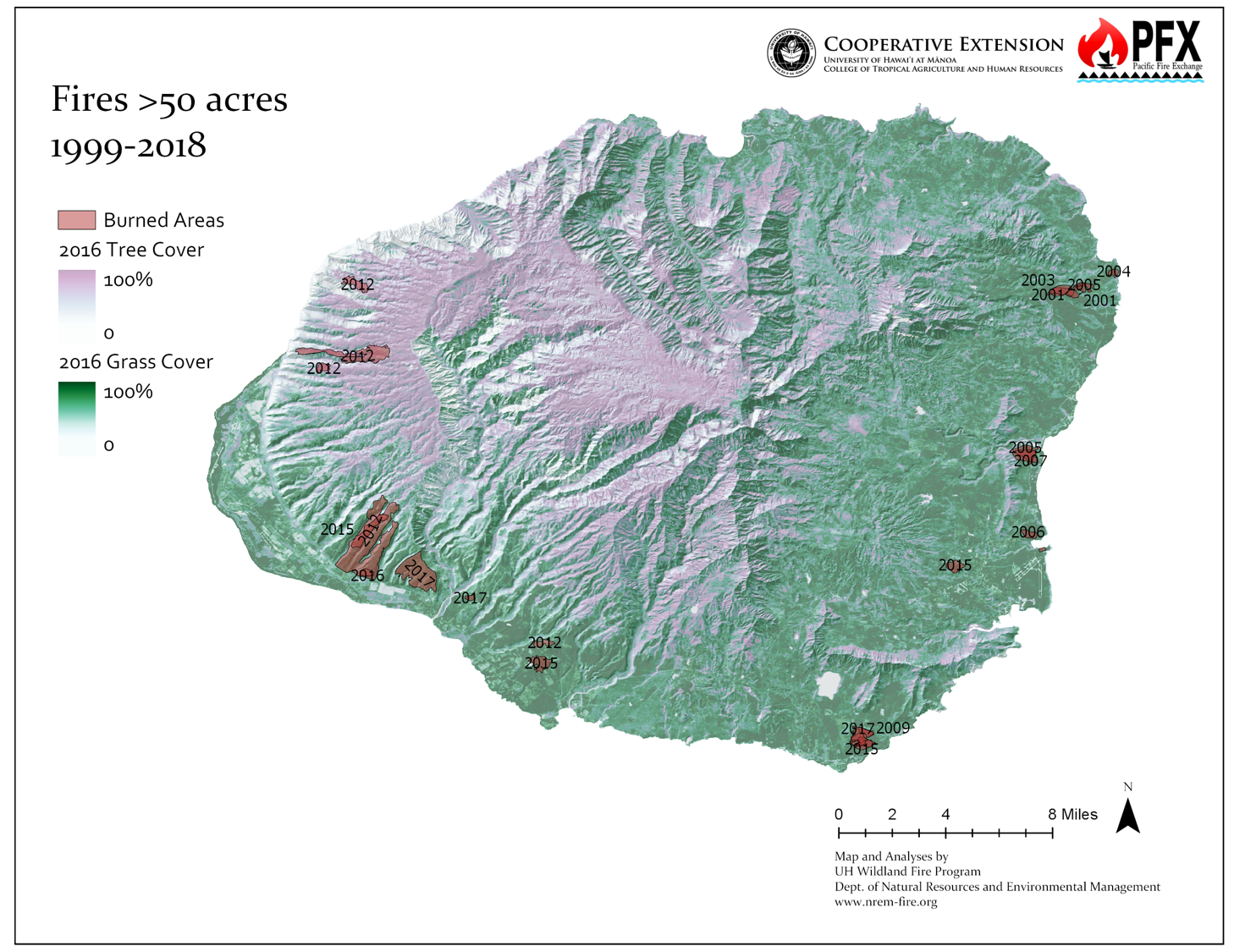
Ignitions occur regularly in the inhabited areas of the island, mostly near the coasts, where the landscape is dominated by current and former agricultural lands as well as grass and brush.
Kauaʻi is among the oldest high Hawaiian Islands and has been shaped by significant erosion, creating its dramatic landscape of valleys. Some of the steepest and least accessible areas include the North Shore to the West side, which also correspond strongly with the highest concentration of threatened and endangered species. This creates a challenging environment for reaching and containing fires when they occur, and presents a risk to the resident endangered species. >> READ MORE
After fires burn through an area of native vegetation in Hawaiʻi, the rebounding vegetation is generally dominated by fast growing non-native grasses and shrubs. Not only does this negatively impact biodiversity, but this can also contribute to erosion and the risk of landslides especially on the steep slopes of Kauaʻi.
The biggest large fires have historically occurred on the lee slope of the eastern flank of Waimea valley. This presents a concerning fire risk for the drought-prone community of Kekaha.
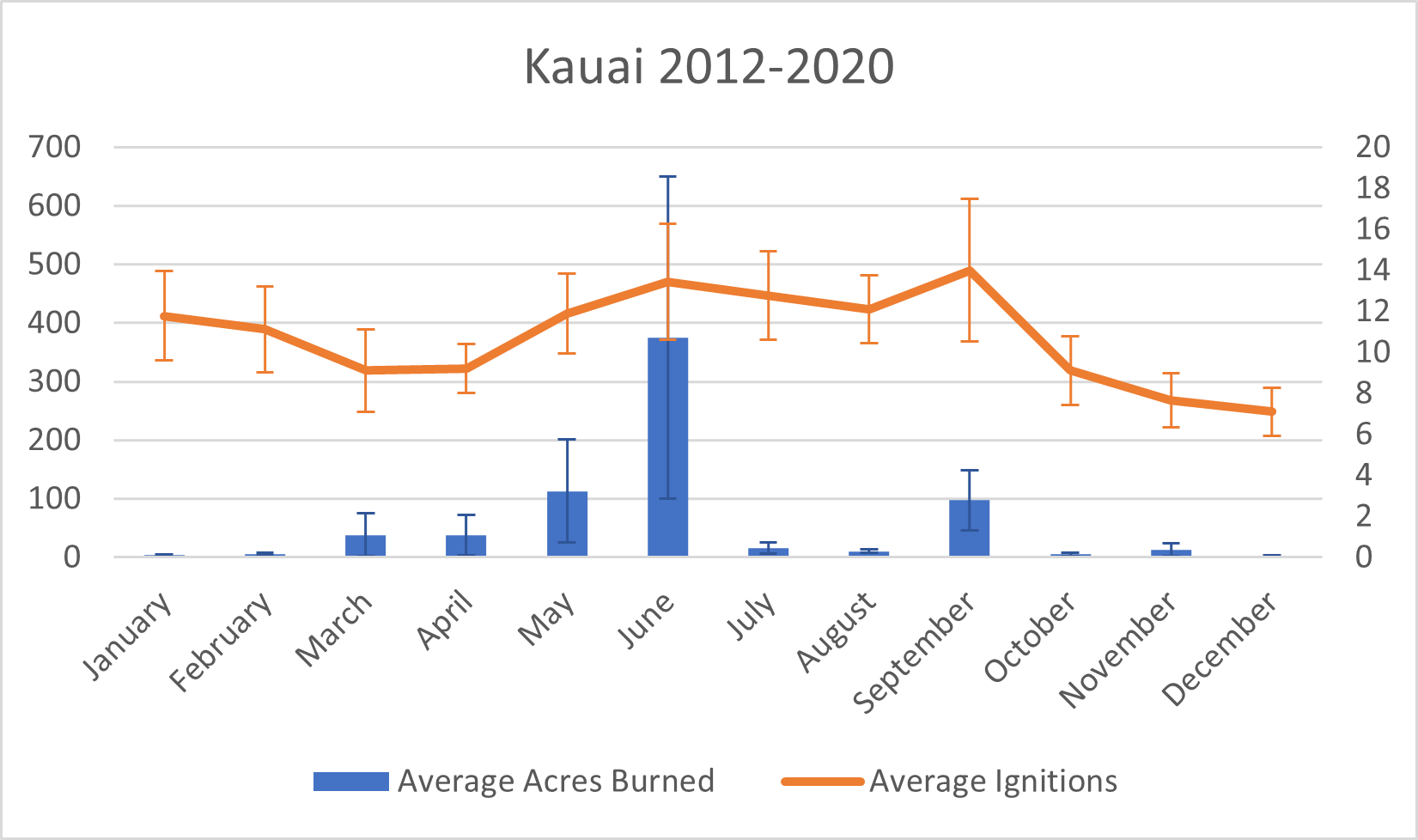
Kauaʻi is known for its high rainfall, but annual rainfall is not always a good indicator for risk. Particularly wet periods over a rainy season can, counterintuitively, significantly elevate hazard levels. Increased precipitation may lead to a surplus of vegetation growth, becoming potential fuel during subsequent drier periods, thereby elevating the risk of large wildfires. Given the changing wind and rainfall patterns arising from climate change, this may lead to increased risk for Kauaʻi.
Recent Resources For Hawai‘i
In this joint webinar hosted by the Pacific Fire Exchange and the Pacific Regional Invasive Species Climate Change, we tackle the climate crisis in Hawai`i and how this affects the risk of wildfire as well as the impacts to people and the archipelago’s unique resources.
In this Pacific Fire Exchange talk story Q&A session, we speak with Dr. Clay Trauernicht and Dr. Alyssa Anderson, University of Hawai`i at Mānoa about wildfire in Hawai`i in the context of Hawaiian language newspapers as well as the historical landscape changes of the 20th century.
In this Pacific Fire Exchange talk story Q&A session, we round up the latest research, past and present for managers and landowners wanting to understand more about how our four-legged friends (goats, sheep, cows, etc.) if managed properly can help reduce blazing and wildland fire. This month’s science share out and conversation was with Dr. Clay Trauernicht, University of Hawai`i at Mānoa Ecosystems and Fire Specialist; Raia Olsen of O‘ahu Grazers and Dr. Elliott Parsons, formerly with the Department of Land and Natural Resources. They presented the how-tos on hiring island professional grazers and lessons learned for contract grazing.