O‘ahu
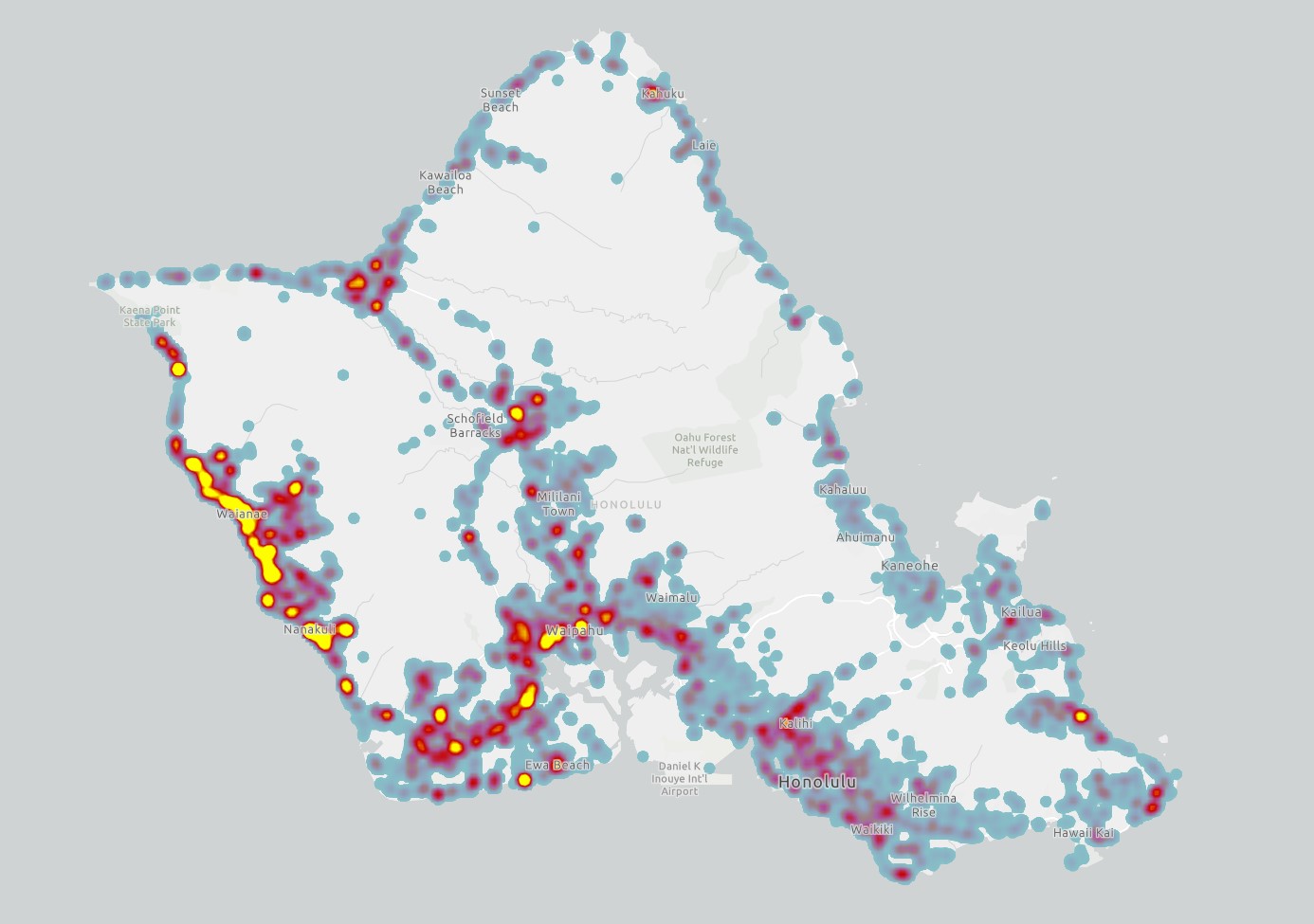
As the most populated island in Hawaiʻi, Oʻahu experiences a significantly higher number of wildfire ignitions than other islands. This elevated ignition rate, coupled with densely populated communities in close proximity to fire-prone shrublands and grasslands, presents a potentially hazardous situation for thousands of residents.
The steep slopes of the Koʻolaupoko and Koʻolauloa regions on the windward side intercept a substantial portion of the moisture from prevailing northeast trade winds, resulting in the distinctive wet windward side and drier lee areas. The most vulnerable areas on the windward side of the island are around Kāneʻohe Bay, where ignitions, winds, and subdivisions bordered by patchy grasslands increase risk, and near drier Kahuku to the north.
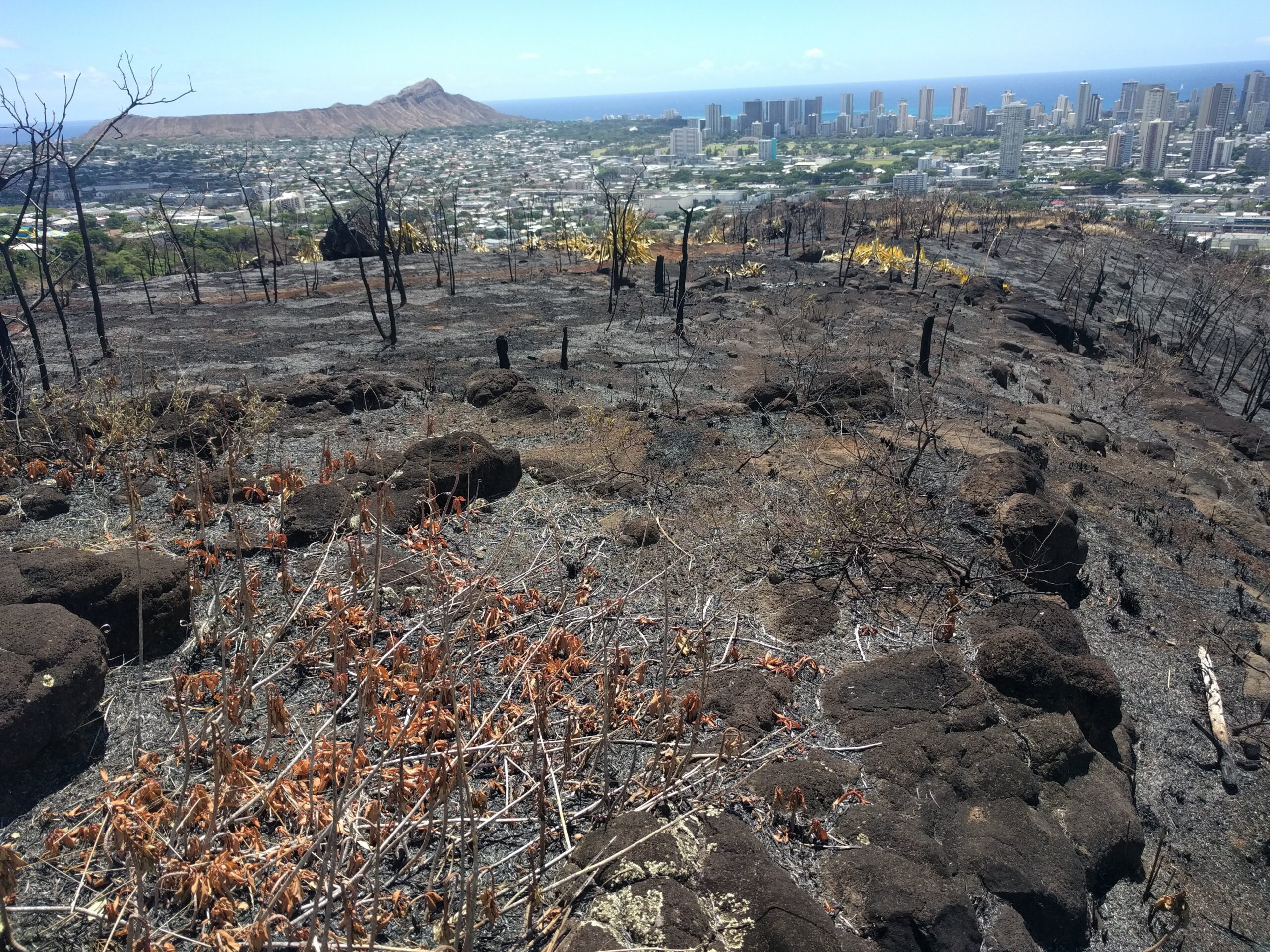
Along the leeward south shore from Pearl City to Hawaiʻi Kai is the island's most densely developed region. These tightly packed neighborhoods extend from the coastline into the heads of valleys, often bordering numerous fire-prone shrublands and grasslands, exposing residents to increased wildfire risk. Hawaiʻi Kai, in particular, is exposed to trade winds originating from the north, which wrap around the eastern tip of the island. Furthermore, Hawaiʻi Kai is adjacent to lowland areas dominated by non-native vegetation in grasslands and shrublands, as well as cliffs and ridges that may experience periods of drought.
The central region of Oʻahu stretching from Waipahu to the Haleʻiwa on the North Shore, lies between the Koʻolau mountains to the west and Waiʻanae range to the east. This area contains both well-developed urban areas and the island's most extensive region of current and former agricultural lands. This wildland-urban-interface is at greatest wildfire risk for loss of property, life, and natural resources.
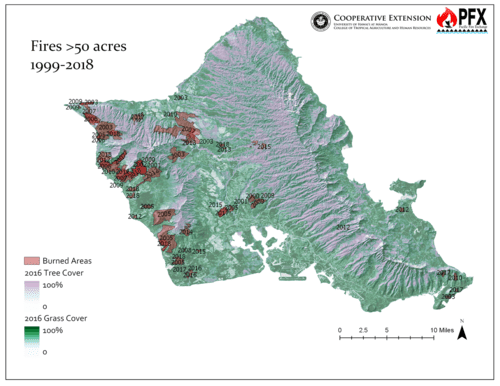
Western Oʻahu, on the lee side of the Waiʻanae mountains, is where the most frequent large fires have occurred. Fires starting in the lowlands near human infrastructure, effectively “erode” the edges of upland forested areas, which become replaced by grasses and increase the risk of fire over time. Unfortunately this intersects with the highest density of threatened and endangered species on Oʻahu. Several notable fires have extinguished populations of various native, endangered species including the 2007 Waialua fire which destroyed a population of the Hawaiʻi state flower, maʻo hau hele, and the 2018 Keaau fire which destroyed one of the largest stands of wiliwili trees.
Recent Resources For Hawai‘i
Learn the perspectives of Amy Tsuneyoshi and Kaimana Wong from the Honolulu Board of Water Supply (HBWS) and Mikaela Bolling from the Waianae Mountain Watershed Partnership (WMWP) with respect to fire breaks and fire prevention.
Fountain grass is an invasive, highly flammable ornamental plant that has overtaken the dry, tropical ecosystems of west Hawaii. Over the last several decades, large, fast spreading fountain grass fires have burned across the landscape with increasing frequency, usually ignited by roadside activities in remote areas. The Pu’u Anahulu Fuels Management Project evaluated the effectiveness of different roadside fuels treatments on fountain grass using a collaborative approach, and allowed the first use of science-based fuels treatments and prescribed fire in Hawaii. Demonstration sites were established along roadsides where ignitions were known to occur. The clear winner for sustained reduction of fountain grass was a three stage application of prescribed fire, grazing and herbicide.
This project was developed and carried out by SWCA Environmental Consultants (SWCA) to determine the effectiveness of three different methods in reducing the surface fuel loads in a guinea grass (Panicum maximum) dominated community, thereby reducing susceptibly to sustained fires. Three control treatments were tested including mechanical removal, herbicide application and grazing using cattle to reduce the fuel loads at Marine Corps Training Area Bellows (MCTAB), on the island of O‘ahu, Hawai‘i. Information on the cost of the various control treatments and their long-term effectiveness in maintaining reduced fuel loads would also benefit land and resource managers in the Pacific Islands where guinea grass and frequent fires are problematic.