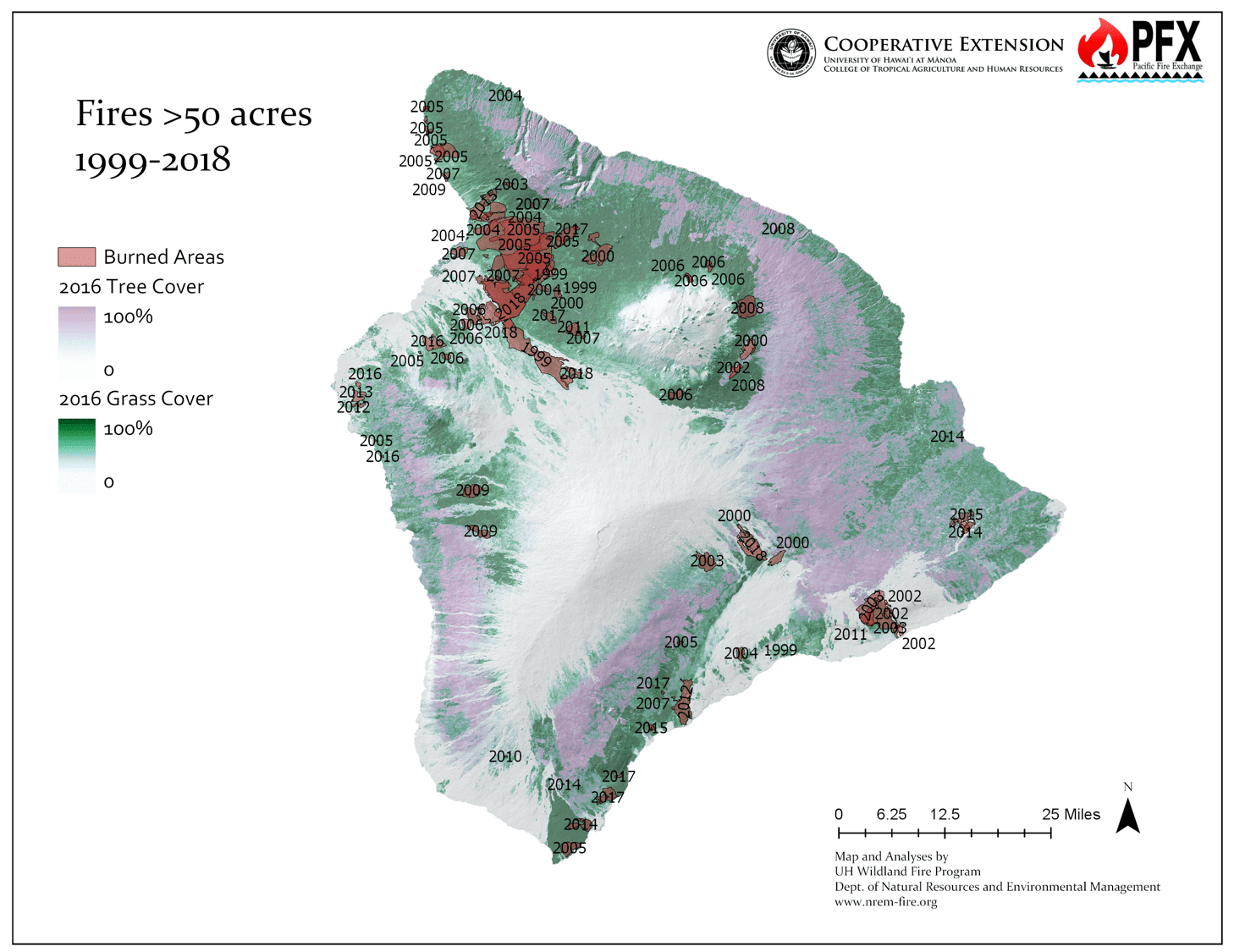
Hawai‘i Island
Hawaiʻi Island is unique in that it is the only Hawaiian island with ongoing active volcanic eruptions. However, humans are still by far the leading cause of wildfire ignitions. The majority of wildfires on Hawaiʻi Island are caused by human error or arson, especially near developments, power line right of ways, and along roadsides.
Fire Today
Rainfall follows the typical pattern of the Hawaiian Islands, with more rain along the eastern windward coast. Mauna Kea and Mauna Loa create a rain shadow that results in drier conditions on the western leeward coasts. Most of the former sugar plantation lands are on the wetter windward side of the island, along the Hāmākua Coast. Despite this location, there is a long history of fires in the area. It was the large 1901 Hāmākua coast fire that was the impetus for keeping wildfire records in Hawaiʻi. >> READ MORE
On the leeward side, the Kohala area is particularly fire-prone. This drier region with large areas of fallow pasture and agricultural land has a high rate of ignitions vis-a-vis human infrastructure, as well as more regular large fires.
The growing footprint of these grass-dominated fallow agricultural lands combined with increasing human population increases the risk of wildfire across the island. The hazardous vegetation and high number of ignitions is exacerbated by climate change creating more frequent drought conditions.
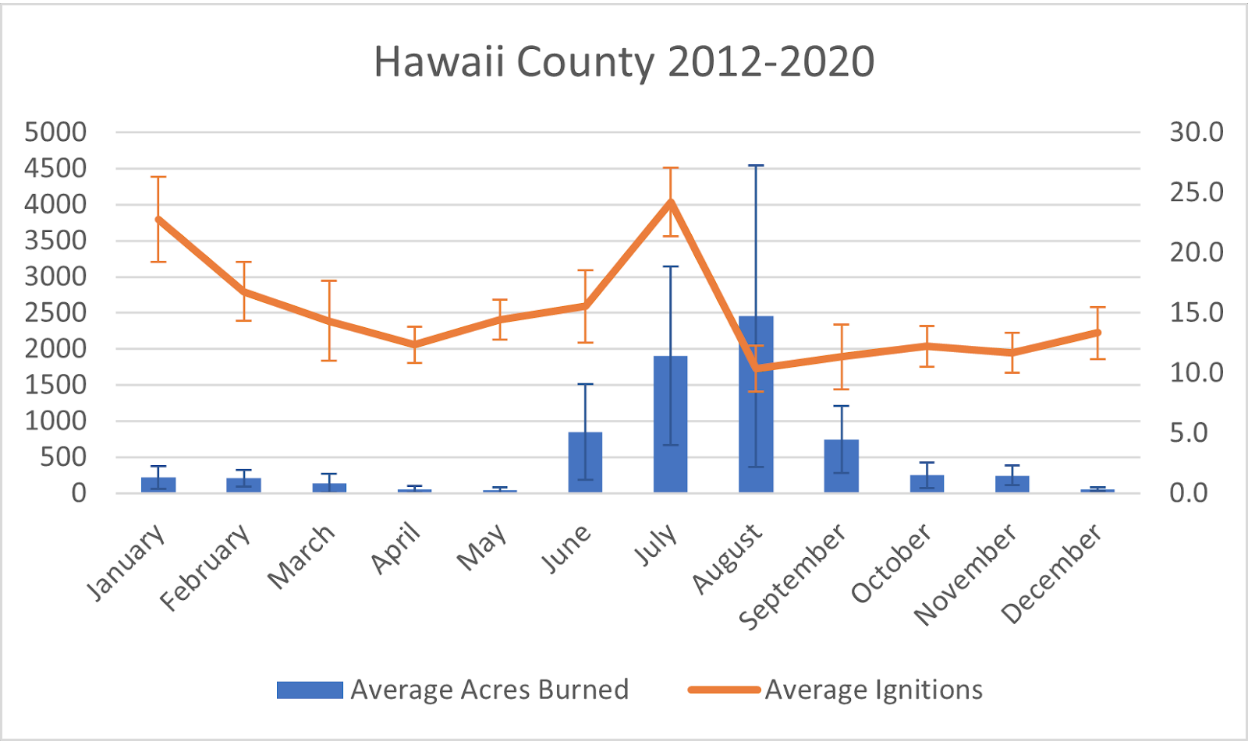
Seasonal variation in rainfall also affects both ignitions and the extent of areas which burn. Particularly wet periods over a rainy season can, counterintuitively, significantly elevate hazard levels. Increased precipitation may lead to a surplus of vegetation growth, becoming potential fuel during subsequent drier periods, thereby elevating the risk of large wildfires. Given the changing wind and rainfall patterns arising from climate change, this may lead to increased risk.
Recent Resources For Hawai‘i
The native Hawaiian dryland forests of the Wai`anae Mountains are home to many unique species that are disappearing. Among the many threats facing dryland forests throughout the islands, the one that is perhaps most serious – and most preventable – is wildfire. (Produced by Outside Hawai’i, a program of Mālama Learning Center – 5 min)
Methodology of weed fire risk assessments. University of Hawai’i at Mānoa’s Kevin Faccenda and Curt Daehler developed a screening system focused on wildfire risk by asking land managers to assign a relative fire…
As Hawai‘i land managers know all too well, natural and cultural resource stewardship can be a daunting undertaking involving many stakeholders from different backgrounds taking into account complex social, cultural, and ecological considerations. In this webinar, UH Mānoa Masters student Rachael Cleveland demonstrates the utility of a decision support tool called Fuzzy Cognitive Mapping (FCM) which enables all stakeholders to create a “mental map” that can capture and compute the impacts of various decision-making scenarios on important resources. Land managers will learn how the FCM software works and its application to a wildfire group in Wai`anae, Hawai‘i whom she interviewed as part of her research.