Fire History of the Region
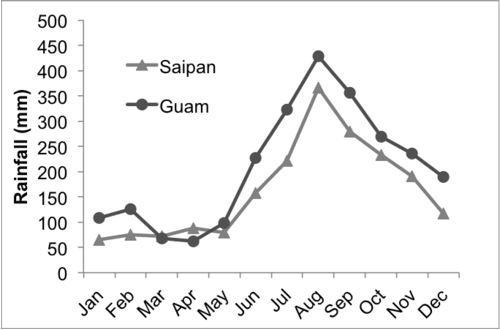
Human-caused wildland fires occur annually in Guam and the inhabited Northern Mariana Islands - Rota, Saipan, and Tinian. Fire has been identified as a key threat to communities, forest resources and watershed integrity in the 2010-2015 Statewide Resource Assessment and Strategies for both regions. Fire records on Guam from 1979-2000 show that an average of 730 fires per year burned 4,800 acres (1,942 ha), or c. 4% of the island's total land area. Annual fire number and area burned increased in years following El Niño events.
Wildfire Today
The cause of the majority of fires is attributed to intentional burning, typically related to hunting activities. In addition, fire-prone savanna vegetation accounts for 17-23% of the main islands in the Marianas chain. Fire occurrence is most frequent during the pronounced dry season from December to June.

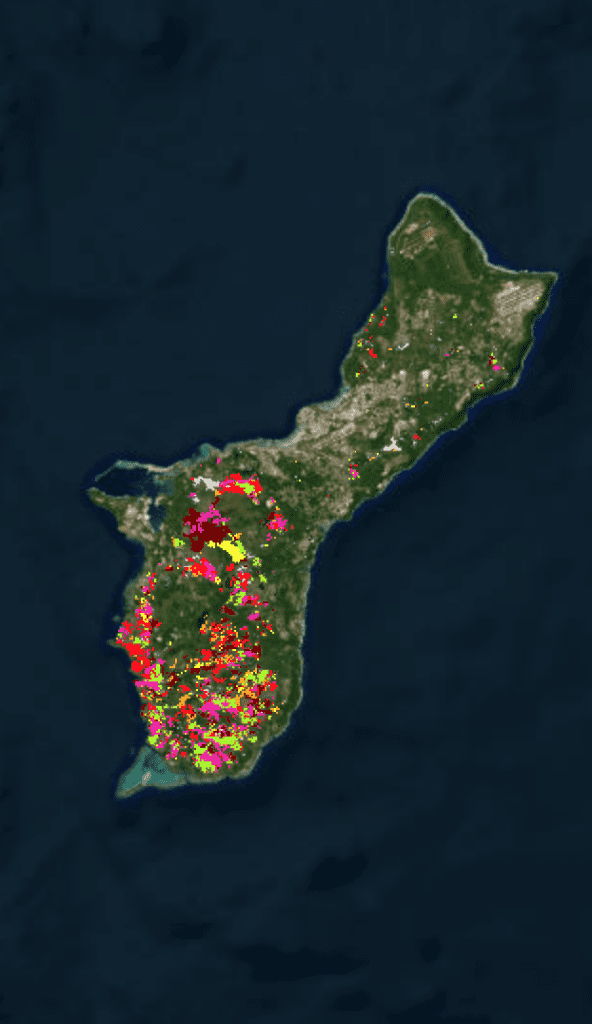
Guam & CNMI Fires
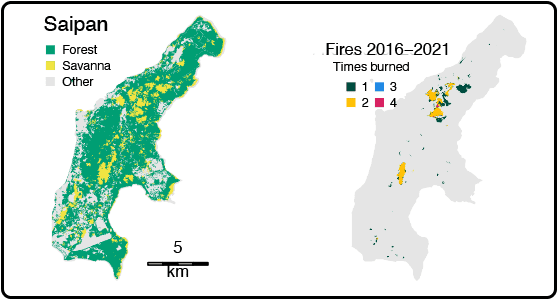
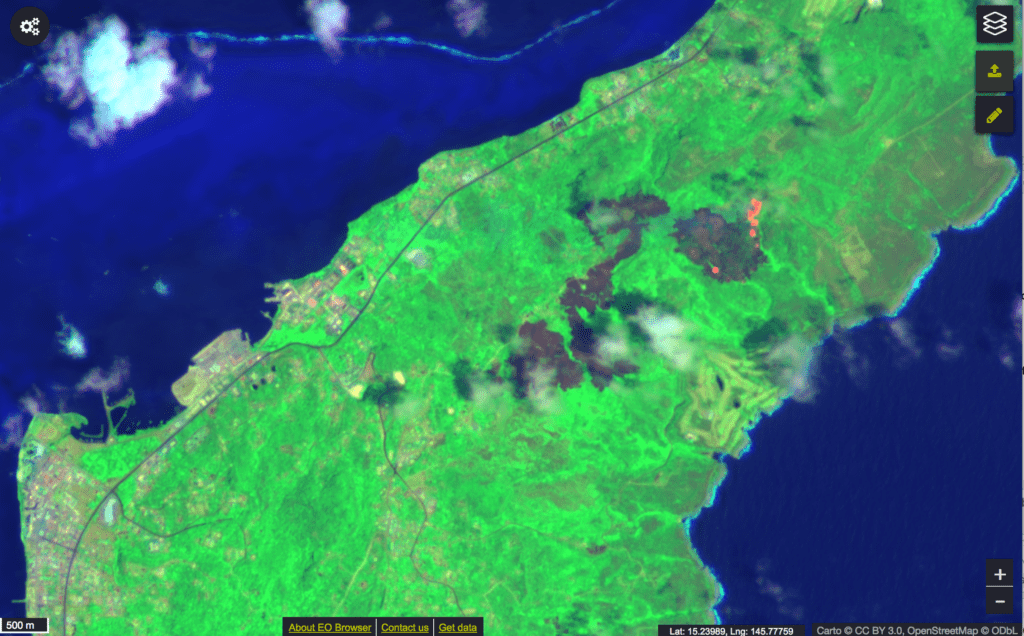
The US Forest Service’s Pacific Island Research Center’s Julian Dendy has mapped the extent of wildfires from 2015 – 2022.
Recent Resources for the Western Pacific
When re-planting, limit the spread of invasive pests by following these guidelines.
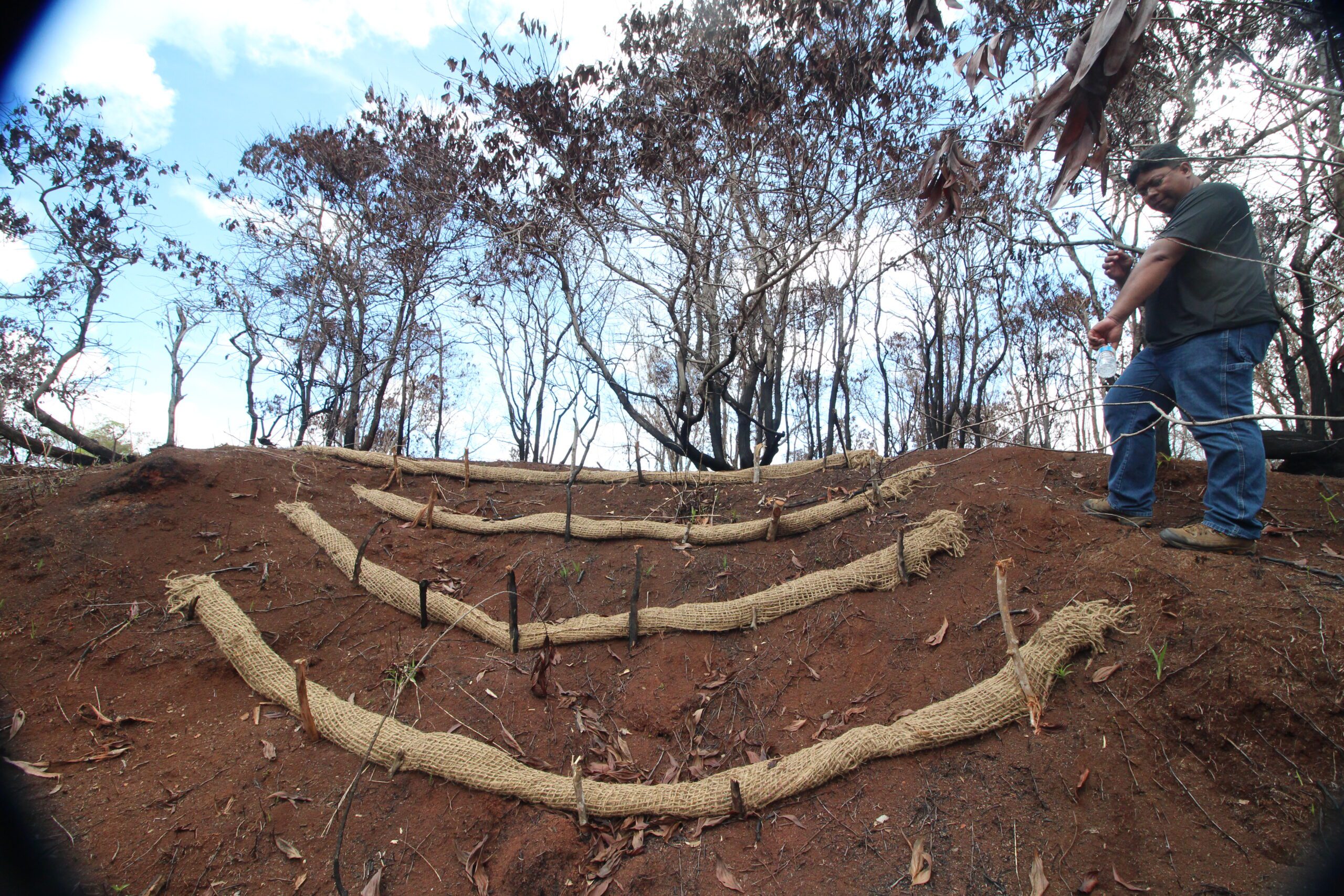
In the aftermath of evacuation and recovery, communities and responders are often dealing with hazardous environmental conditions which call for vigillant public safety and environmental stabilization.
The role that farms and ranches play in land care is critical across fire prone landscapes. Ranches and farms keep fire-prone weeds at bay to maintain pastures and crops.



